Campbell Biology 9th Edition Test Bank Chapter 6
1
1) In the fractionation of homogenized cells using centrifugation, the primary factor that determines whether a specific cellular component ends up in the supernatant or the pellet is the___.
a) Percentage of carbohydrates in the component
b) Presence or absence of lipids in the component
c) Relative solubility of the component
d) size and weight of the component
2
2) The advantage of light microscopy over electron microscopy is that___.
a) Light microscopy allows one to view dynamic processes in living cells
b) light microscopy provides for higher magnification than electron microscopy
c) light microscopy provides higher contrast than electron microscopy
d) light microscopy provides for higher resolving power than electron microscopy
3
3) Which of the following macro-molecules leaves the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell through pores in the nuclear membrane?
a) DNA
b) phospholipids
c) glycogen
d) mRNA
4
4) Large number of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in producing which of the following molecules?
a) Nucleic acids
b) proteins
c) glycogen
d) lipids
5
5) The Golgi apparatus has a polarity, or sidedness to its structure and function. Which of the following statements correctly describes this polarity?
a) Lipids in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other
b) Transport vesicles fuse with one side of the Golgi and leave from the opposite side
c) proteins in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other
d) All of the listed responses correctly describe polarity characteristics of the Golgi function.
6
6) Cyanide binds with at least one molecule involved in producing ATP. If a cell is exposed to cyanide, most of the cyanide will be found within the___.
a) Mitochondria
b) lysosomes
c) peroxisomes
d) endoplasmic reticulum
7
7) The evolution of eukaryotic cells most likely involved__.
a) Anaerobic archaea taking up residence inside a large bacterial host cell to escape toxic oxygen-the anaerobic bacterium evolved into chloroplasts
b) acquisition of an endomembrane system and subsequent evolution of mitochondria from a portion of the Golgi
c) endosymbiosis of an aerobic bacterium in a larger host cell – the endosymbiont evolved into mitochondria
d) an endosymbiotic fungal cell evolving into the nucleus
8
8) Researches tried to explain how vesicular transport in cells by attempting to assemble the transport components. They set up microtubular tracks along which vesicles could be transported, and they added vesicles and ATP (because they knew the transport process requires energy). Yet, when they put everything together there was no movement or transport of vesicles. What were they missing?
a) Endoplasmatic reticulum
b) motor proteins
c) contractile microfilaments
d) an axon
9
9) The cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and plant cells an the extracellular matrix cells are all external to the plasma membrane. Which of the following is a characteristic common to all of these extracellular structures?
a) They must block water and small molecules to regulate the exchange of matter and energy with their environment
b) they are composed of a mixture of lipids and nucleotides
c) they must provide a rigid structure that maintains an appropriate ratio of cell surface area to volume
10
10) Suppose a young boy is always tired and fatigued, suffering from a metabolic disease. Which of the following organelles is most likely involved in this disease?
a) Golgi apparatus
b) mitochondria
c) ribosomes
d) lysosomes
11
11) Spherocytosis is a human blood disorder associated with a defective cytokeletal protein in the blood cell (RBCs). What do you suspect is the consequence of such a defect?
a) Abnormally shaped RBCs
b) adherence of RBCs to blood vessel walls, causing plaque formation
c) an insufficient supply of oxygen-transportation proteins in the RBCs
d) an insufficient supply of ATP in the RBCs
12
12) H.V. Wilson worked with sponges to gain some insight into exactly what was responsible for holding adjacent cells together. He exposed two species of differently pigmented sponges to a chemical that disrupted the cell-cell interaction (cell junctions), and the cells of the sponges dissociated. Wilson then mixed the cells of the two species and removed the chemical that caused the cells to dissociate. Wilson found that the sponges reassembled into two separate species. The cells from one species did not interact or form associations with the cells of the other species. How do you explain the results of Wilson's experiments?
a) One cell functioned as the nucleus for each organism, thereby attracting only cells of the same pigment
b) The molecules responsible for cell-cell adhesion (cell junctions) were irreversibly destroyed during the experiment.
c) The molecule responsible for cell-cell adhesion (cell junctions) differed between the two species of sponge
d) The two species of sponge had different enzymes that functioned in the reassembly process.
13
13) For a protein to be an integral membrane protein, it would have to be __.
a) exposed on only one surface of the membrane
b) hydrophilic
c) amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region
d) hydrophobic
14
14) The membranes of winter wheat are able to remain fluid when it is extremely cold by___.
a) Cotransport of glucose and hydrogen
b) decreasing the number of hydrophobic proteins in the membrane
c) increasing the percentage of cholesterol molecules in the membrane
d) increasing the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in the membrane.
15
15) Singer and Nicolson's fluid mosaic model of the membrane proposed that membranes____.
a) consist of protein molecules embedded in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids.
b) consist of a mosaic of polysaccharides and proteins.
c) are a phospholipid bilayer between two layers of hydrophilic proteins.
d) are a single layer of phospholipids and proteins.
16
16) An animal cell lacking oligosaccharides on the external surface of its plasma membrane would likely be impaired in which function?
a) attaching the plasma to the cytoskeleton
b) cell-cell recognition
c) establishing the diffusion barrier to charged molecules
d) transporting ions against an electrochemical gradient
17
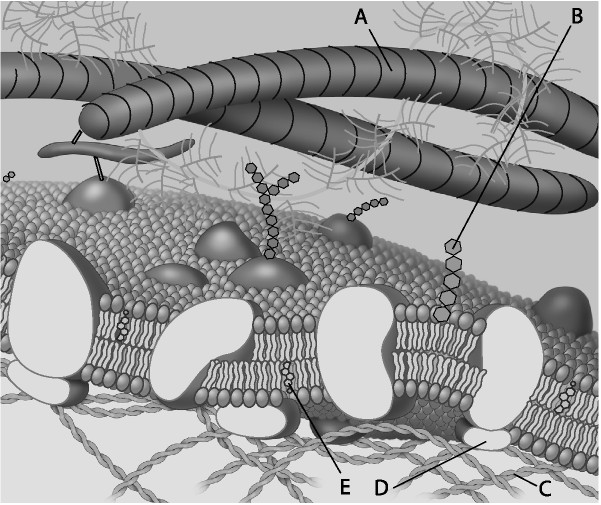
For the following question, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description
17) Which component is a peripheral protein?
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
18
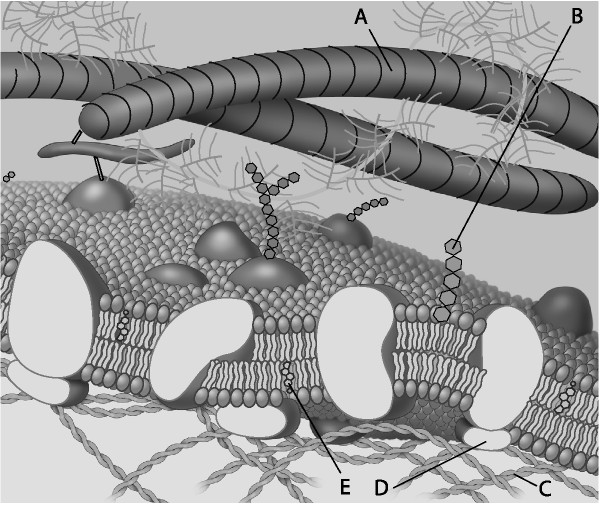
18) Which component is cholesterol?
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
19
19)Which of the following allows water to move faster across cell membranes?
a) Aquaporins
b) the sodium-potassium pump
c) peripheral proteins
d) ATP
20
20)Which of the following would likely move through the lipid bilayer of a plasma membrane most rapidly?
a) An amino acid
b) glucose
c) K+
d) CO2
21
21) Which of the following processes includes all other?
a) Passive transport
b) transport of an ion down its electrochemical gradient
c) osmosis
d) facilitated diffusion
22
22) You are working on a team that is designating a new drug. For this drug to work, it must enter the cytoplasm of specific target cells. Which of the following would be a factor that determines whether the molecule selectively enters the target cells?
a) Lipid composition of the target cell's plasma membrane
b) similarity of the drug molecule to other molecules transported by the target cells
c) hydrophobicity of the drug molecule
d) lack of charge on the drug molecule
23
23) Which of the following is true of osmosis?
a) Osmosis only takes place in red blood cells
b) In osmosis, water moves across a membrane from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration
c) In osmosis, solutes move across a membrane from areas of lower water concentration to areas of higher water concentration
d) Osmosis is an energy-demanding or "active" process
24
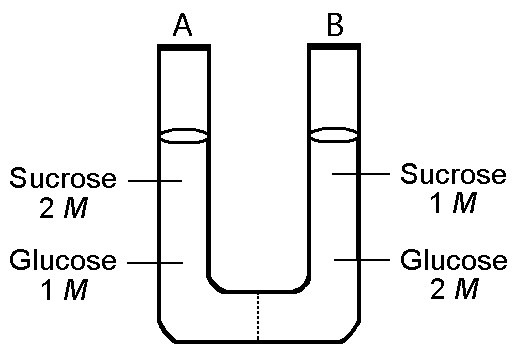
The solution in the two arms of this U-tube are separated by a membrane that is permeable to water and glucose but not to sucrose. Side A is half-filled with a solution of 2 M sucrose and 1 M glucose. Side B is half-filled with 1 M sucrose and 2 M glucose. Initially, the liquid levels on both sides are equal.
24) Refer to the figure. Initially, in terms of tonicity, the solution in side A with respect to that in side B is
a) saturated
b) hypertonic
c) hypotonic.
d) Isotonic
25
25) A patient was involved a serious accident and lost a large quantity of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water - equal to the volume of blood lost – is added to the blood directly via one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion?
a) The patient's red blood cells will burst because the blood has become hypertonic compared to the cells.
b) The patient's red blood cells will swell and possibly burst because the blood has become hypotonic compared to the cells.
c) The patient's red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood has become hypotonic compared to the cells.
d) The patient's red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood has become hypertonic compared to the cells.
26
26) Most cells cannot harness heat to perform work because___
a) heat is not a form of energy
b) heat can never be used to do work
c) heat must remain constant during work
d) temperature is usually uniform throughout a cell
27
27) Which of the following involves a decrease in entropy?
a) Reactions that separate monomers
b) depolymerization reactions
c) hydrolysis reactions
d) condensation reactions
28
28)Which of the following statements is a logical consequence of the second law of thermodynamics?
a) Every chemical reaction must increase the total entropy of the universe
b) energy can be transferred or transformed, but it cannot be created o destroyed
c) if the entropy of a system increases there must be a corresponding decrease in the entropy of the universe
d) if there is an increase in the energy of a system, there must be a corresponding decrease in the energy of the rest of the universe
29
29) Which of the following types of reactions would decrease the entropy within the cell?
a) Catabolic reactions
b) digestion
c) anabolic reactions
d) hydrolysis
30
30) Biological evolution of life on Earth, from simple prokaryote-like cells to large multicellular eukaryotic organisms ___.
a) has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics.
b) has been made possible by expending Earth's energy resources.
c) has occurred in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics, by expending Earth's energy resources and causing an increase in the entropy of the planet.
d) has caused an increase in the entropy of the planet.
31
31) You have discovered an enzyme that can catalyze two different chemical reactions. Which of the following is most likely to be corrected?
a) Either the enzyme has two distinct active sites or the reactants involved in the two reactions are very similar in size and shape.
b) The enzyme is subject to competitive inhibition and allosteric regulation.
c) The enzyme contains α-helices and β-pleated sheets.
d) Two types of allosteric regulation occur: The binding of one molecule activates the enzyme, while the binding of a different molecule inhibits it.
32
32) A chemical reaction that has a positive G is best described as____.
a) Spontaneous
b) exergonic
c) endergonic
d) enthalpic
33
33) The active site of an enzyme is the region that____
a) is inhibited by the presence of a co-enzyme or a co-factor
b) binds noncompetitive inhibitors of the enzyme
c) is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme.
d) binds allosteric regulators of the enzyme.
34
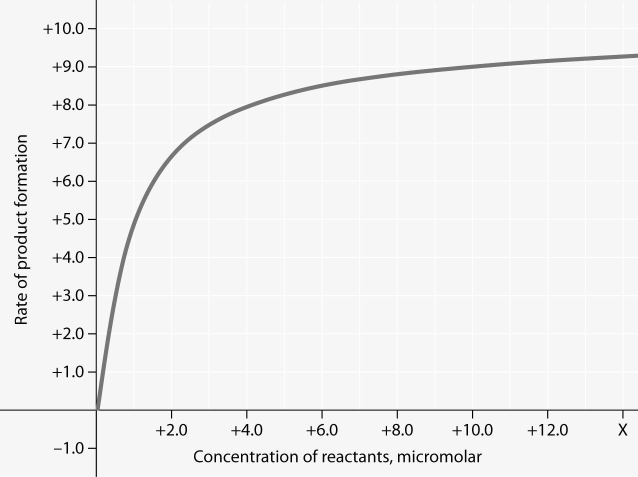
Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant concentration, with the concentration of enzyme constant
34) In the figure, why does the reaction rate plateau at higher reactant concentrations?
a) The reaction nears equilibrium at high reactant concentrations.
b) Feedback inhibition by product occurs at high reactant concentrations.
c) Most enzyme molecules are occupied by substrate at high reactant concentrations.
d) The rate of the reverse reaction increases with reactant concentration.
35
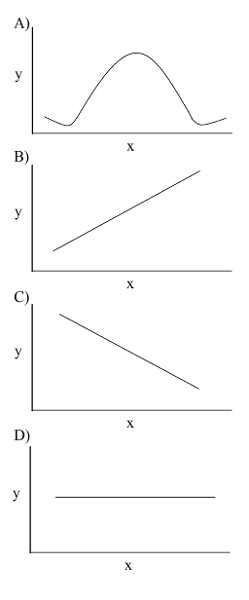
35) You collected data on the effect of pH on the function of the enzyme catalase in human cells. Which of the following graphs would you expect?
a) A
b) B
c) C
d) D
36
36) Substrate level phosphorylation occurs___
a) in glycolysis
b) in the citric acid
c) during oxidative phosphorylation
d) in both glycolysis and the citric acid
37
37) Which of the listed statements describes the results of the following reaction?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy
a) CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized.
b) C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
c) O2 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized.
d) O2 is oxidized and H2O is reduced.
38
38) When a molecule of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) gains a hydrogen atom (not a proton), the molecule becomes_____.
a) Redoxed
b) dehydrogenated
c) oxidized
d) reduced
39
39) Which of the following statements about NAD+ is true?
a) Is the absence of NAD+, glycolysis can still function
b) NAD+ has more chemical energy than NADH
c) NAD+ is reduced to NADH during glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle
d) NAD+ can donate electron for use in oxidative phosphorilation
40
40) Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percentage of the ATP formed by the reactions of glycolysis?
a) 100%
b) 0%
c) 38%
d) 2%
41
41) In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate____
a) two molecules of ATP are used and six molecules of ATP are produced.
b) two molecules of ATP are used and four molecules of ATP are produced.
c) two molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced.
d) four molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced.
42
42) Carbon dioxide (CO2) is released during which of the following stages of cellular respiration?
a) glycolysis and the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
b) oxidative phosphorylation and fermentation
c) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the citric acid cycle
d) fermentation and glycolysis
43
43) During aerobic respiration H2O is formed. Where does the oxygen atom for the formation of the water come from?
a) pyruvate (C₃H₃O₃-)
b) glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)
c) molecular oxygen (O₂)
d) carbon dioxide (CO₂)
44
44) The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to ____
a) combine with lactate forming pyruvate
b) combine with carbon, forming CO2
c) yield energy in the form of ATP as it is passed down the respiratory chain
d) act as an acceptor for electron and hydrogen, forming water
45
45) Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located?
a) mitochondrial inner membrane
b) mitochondrial matrix
c) mitochondrial outer membrane
d) mitochondrial intermembrane space
46
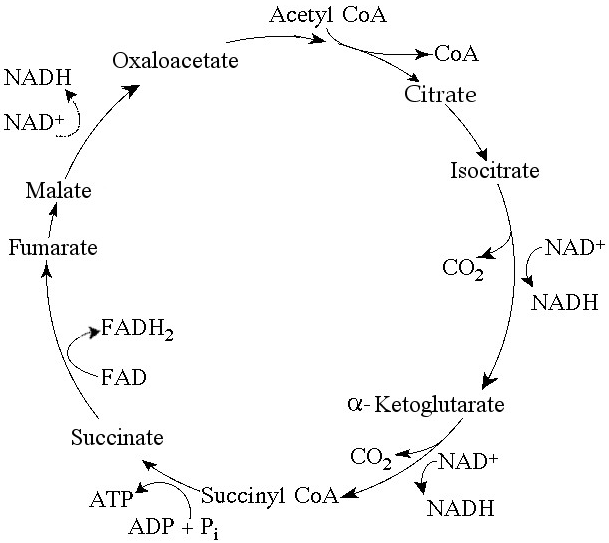
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
46) Starting with citrate, which of the following combinations of products would result from three acetyl CoA molecules entering the citric acid cycle ( see the accompanying figure)?
a) 3 ATP, 6 CO₂, 9 NADH, and 3 FADH₂
b) 1 ATP, 2 CO₂, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH₂
c) 38 ATP, 6 CO₂, 3 NADH, and 12 FADH₂
d) 3 ATP, 3 CO₂, 3 NADH, and 3 FADH₂
47
47) Which of the following events tales place in the electron transport chain?
a) substrate-level phosphorylation
b) breakdown of glucose into two pyruvate molecules.
c) the breakdown of an acetyl group to carbon dioxide
d) the extraction of energy from high-energy electrons remaining from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
48
48) You have a friend who lot 7 kg (about 15 pounds) of fat on a regimen of strict diet and exercise. How did the fat leave his body?
a) It was converted to ATP, which weighs much less than fat.
b) It was converted to urine and eliminated from the body.
c) It was converted to heat and then released.
d) It was released as CO₂ and H₂O.
49
49) Chemiosmotic ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation) occurs in ____
a) only in mitochondria, using either oxygen or other electron acceptors.
b) all cells, but only in the presence of oxygen.
c) all respiring cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, using either oxygen or other electron acceptors.
d) only eukaryotic cells, in the presence of oxygen.
50
50) Which of the following normally occurs regardless of whether or not oxygen (O2) is present?
a) Glycolysis
b) oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)
c) citric acid cycle
d) fermentation
51
51) What part of the cell is essential to aerobic respiration?
a) Ribosomes
b) mitochondrion
c) endoplasmatic reticulum
d) nucleus
Campbell Biology 9th Edition Test Bank Chapter 6
Source: https://www.easynotecards.com/notecard_set/41481